In the vast and ever-evolving world of cryptocurrency, investors and enthusiasts must exercise caution to protect themselves from fraudulent projects. Projects operating in the DePIN space are no different in this respect. This guide looks into the key red flags that can help you identify and avoid DePIN scam projects. By staying vigilant and informed, you can safeguard your investments and contribute to legitimate projects. It’s important keep in mind many startup projects are “building the plane as they fly it” as they say. Many parts may still be in development or immature. Also, some projects fail, not because they are scams, but because they are a ‘terrible idea’ or a poorly executed good one. There’s a difference between unethical behavior (a scam) and incompetence.
Disclaimer: The example screenshots provided are for general reference of potential flags and research methods employed and do not necessarily mean they come from a ‘scam’ project.
Here are some signs or ‘red flags’ of an illegitimate project:
Non-Doxxed Team or Nonexistent Online Presence:
One of the initial red flags to watch out for is a lack of transparency regarding the project’s team. If the team members are not publicly identifiable or their online presence is virtually nonexistent, it raises suspicions about their legitimacy. It is almost impossible in this day and age to not have some online footprint, and this would be even less likely for someone operating in the tech sector. Reputable projects typically have a visible and accessible team with professional backgrounds and verified social media profiles. Conduct thorough research to ensure the team members have a track record of credibility and expertise in their respective fields. It is very easy to use AI to produce realistic images and profiles.
Lack of Originality, Misrepresentation and False Claims:
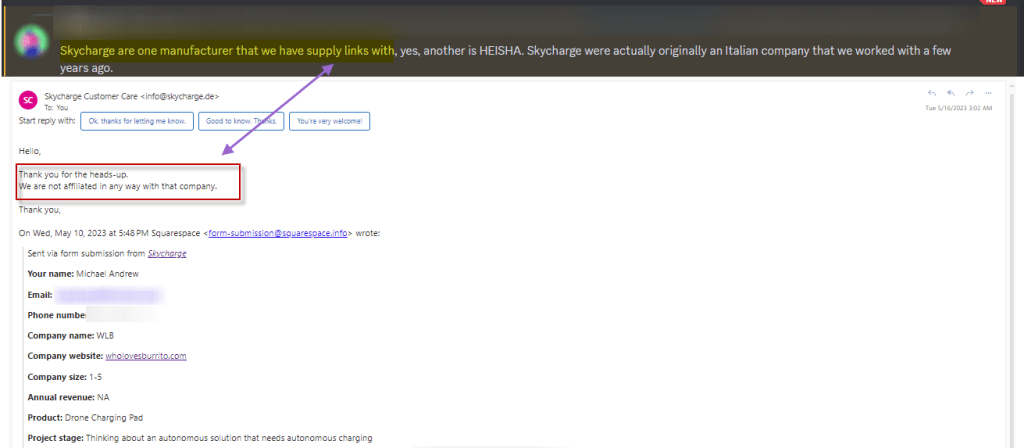
Legitimate projects prioritize originality and integrity in their endeavors. They invest time and effort into developing unique concepts, designs, and products. However, scam projects lack the creativity and dedication needed to create something truly original. By resorting to stealing images or products, they demonstrate a lack of integrity and a disregard for ethical practices. When scammers steal images or products, they often use them to mislead potential investors or users. They may present these stolen assets as their own, making false claims about the capabilities, features, or partnerships associated with their project. This misrepresentation is a deliberate attempt to deceive and manipulate individuals into trusting and investing in their fraudulent venture. Note is it entirely possible that one project or OEM may be a supplier to another project. However, as noted elsewhere, it is generally easy to validate a supplier partnership.
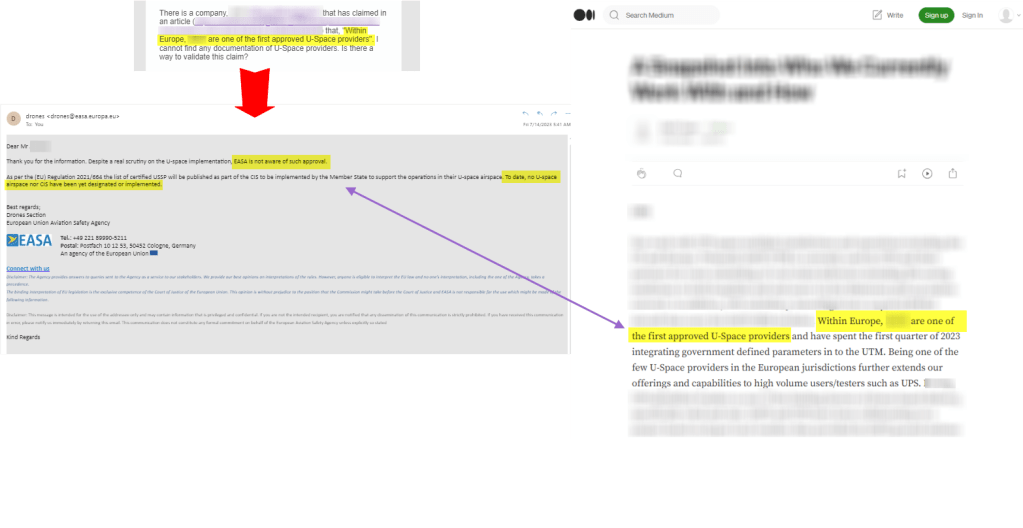
Claims of Partnerships, Certifications, or Approvals That Can’t Be Verified:
One common tactic employed by scam projects is the inclusion of claims of partnerships with government entities or prominent private organizations on their websites or blogs. Or to claim a specific approval or certification (e.g. ‘approved service provider’). These claims are intended to lend credibility to the project and create an illusion of legitimacy. However, it is crucial to approach such claims with skepticism and undertake thorough verification. Here’s why:
- Lack of Verifiable Proof: When confronted with requests for proof of their alleged partnerships, scammers often resort to evasive responses. They may claim that they are not permitted to disclose specific details or hide behind technical jargon to confuse potential investors. In reality, legitimate partnerships are typically backed by tangible evidence that can be verified.
- Transparency and Disclosure: Reputable projects understand the importance of transparency and disclosure, especially when it comes to partnerships. Genuine partnerships are mutually beneficial and involve collaboration between both parties. Consequently, information about these partnerships can be found on both sides, whether it’s through official announcements, press releases, or public statements.

Inconsistent Reward Payouts:
Scam projects often employ deceptive tactics when it comes to rewarding their participants. If a project claims to distribute rewards through prominent cryptocurrency exchanges such as Coinbase but consistently delays or fails to fulfill these payouts, it is a clear warning sign. Reliable projects honor their commitments and ensure timely and consistent distribution of rewards to their participants. Keep in mind, some scams will pay early investors some payouts. The purpose is to get those early investors to talk others into joining as well. Don’t be fooled, getting payments is not necessarily as sign of a legitimate project. Note that if you are in early, it is possible to extract earnings from the project before it disappears. Just keep in mind that is likely not the scammers money, but money from other investors like you. Those at the top of the pyramid, tend to do very well. Also be on lookout for unusual trading schemes (e.g. p2p marketplaces) or lack of liquidity. These can be signs of issues even though legitimate projects may have liquidity issues and have used p2p markets at startup (Helium is an example – though this is generally no longer the case as the market has matured greatly since Helium started).
Constant Delays in Shipping or Non-Functional Hardware:
Another significant red flag to be aware of when assessing projects is a pattern of constant delays in shipping or receiving hardware that doesn’t work as claimed. This can be particularly relevant for projects that involve the production and distribution of physical devices or hardware components. Scam projects often employ tactics to prolong the shipping process or send out subpar hardware that doesn’t meet the promised specifications. They may use these delays as an excuse to buy time or avoid fulfilling their obligations to customers. The longer they can delay, the more time they have to get new investment.
Lack of Proof of Utility for Feasible Technology:
Another important red flag to watch out for when evaluating projects is the lack of proof of utility for a seemingly feasible technology. Scam projects often make grand claims about the capabilities and potential of their technology without providing any substantial evidence or real-world use cases. Legitimate projects in the cryptocurrency space strive to develop innovative solutions that solve real-world problems or address existing inefficiencies. They conduct thorough research and development to ensure their technology is practical, functional, and capable of delivering tangible benefits. However, scam projects may present an impressive-sounding technology without any verifiable proof of its utility. They rely on buzzwords and technical jargon to create an illusion of innovation, while in reality, their technology may be nothing more than smoke and mirrors. For example, a now known scam project IO5, used the DECT 2020 NR technology to try and convince potential project participants it was using a legitimate technology for IOT.
Deletion of Messages and Expulsion of Members Questioning Tech or Economics:
Projects with malicious intent often attempt to silence dissenting voices within their communities. If administrators swiftly delete critical messages or kick out members who raise legitimate concerns about the project’s technological aspects or the clarity of economics, it suggests an environment of secrecy and manipulation. A legitimate project encourages open dialogue and addresses concerns transparently, without resorting to censorship or expulsion. Though it’s important to understand that ‘freedom of speech’ is not a guarantee or a legal requirement for any private project. The developers of a project can run it as they see fit and don’t have to allow you to say whatever you want within their own platforms, but censorship is not a sign of transparency and should elicit caution. Another common tactic is to claim that public communication channels (e.g. Discord channels) are not meant for support and they will push to send emails or use a ticket system. This helps give the perception of an active customer support system while silencing the legitimate FUD.
Inconsistent Support and Constantly Switching Communication Methods:
Inconsistency in support and constantly switching communication methods is another red flag to watch out for when evaluating projects. Legitimate projects understand the importance of providing reliable and accessible support channels to address customer inquiries, concerns, and technical issues. They typically have dedicated support teams and established communication methods to ensure a seamless customer experience. However, scam projects often exhibit inconsistent support practices as a means to avoid accountability or maintain an aura of secrecy. They may frequently switch communication platforms, such as email, Discord, or ticketing systems, indicating that each change is an improvement in their support systems. There can be valid reasons for updating the support methods, but legitimate projects strive to maintain consistent support practices and ensure a positive customer experience, while scams may exhibit more delays, lack of response, inconsistent response, or unhelpful interactions.
Over-Engineered Tokenomics and Wallet Architecture:
Another common characteristic of scam projects is an excessively complicated tokenomics model or wallet architecture. While innovation is an integral part of the cryptocurrency industry, scam projects often use convoluted designs to confuse investors and distract from their lack of substance. Beware of projects that prioritize complexity over utility and fail to provide a clear and concise explanation of their tokenomics or wallet structure.
Investors with a History of Involvement in Other Scams:
Scam projects often attract investors who have a track record of being associated with fraudulent schemes or rug pulls in the past. Research the project’s backers and early investors, and be cautious if you identify individuals with questionable reputations. While individuals can learn from past mistakes and change their behavior, a pattern of involvement in scams should be treated as a significant red flag.
Teams with a Pattern of Overpromising and Under-Delivering:
Consistency is key when it comes to evaluating the credibility of a project. If a team has a history of making grandiose promises but consistently fails to deliver on them, it should raise concerns. Scam projects often use overhyped marketing tactics to lure investors, only to fall short on their commitments. Prioritize projects that demonstrate a track record of meeting milestones and delivering on their promises.
Here are research methods you can employ to further investigate projects:
Reverse Image Searches:
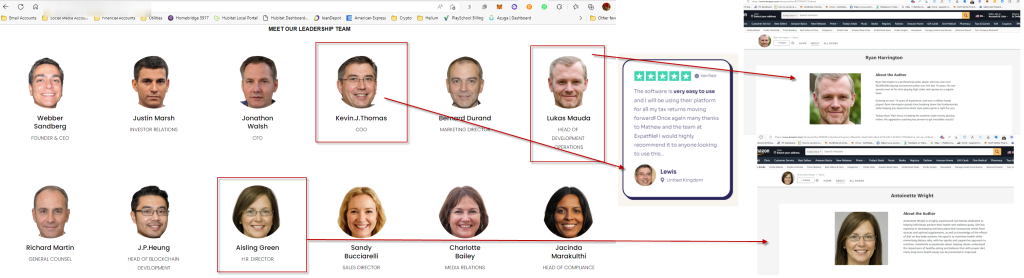
Performing reverse image searches can be a valuable tool in identifying fraudulent projects. Scammers often use stock images, steal the photos of individuals from other sources, or us AI to create fake team member profiles. By using services like Google Images or TinEye, you can upload an image or enter its URL to search for matches across the web. If you find that the team member’s photo appears on multiple unrelated websites or stock image repositories, it indicates a high likelihood of deception. When presented with evidence, scam projects will often make excuses, attempt to hide the information, or even make legal threats to the whistleblowers.
Investigating Service Providers and Partners:
A diligent investor should conduct thorough investigations into the claimed partnerships. Start by researching the alleged service providers or partners to determine their credibility and authenticity. Check for any official announcements or public records that confirm their association with the project. Look for independent sources that corroborate the claimed relationships. Consider reaching out directly to the alleged partners or service providers to inquire about their involvement with the project. Genuine partners are usually open to discussing their collaborations and can provide insights into the nature and extent of their relationship with the project. Be cautious if the project discourages or avoids any attempts to communicate with their claimed partners.
Background Checks on Team Members:
In addition to reverse image searches, conduct thorough background checks on the project’s team members. Search for their names, educational backgrounds, professional experiences, and any notable achievements. Look for publications, industry conferences, or speaking engagements they may have been involved in. Genuine team members usually have a traceable digital footprint with verifiable information, while scam projects often create fictitious identities or use aliases.
Investigate the Claimed Technology:
It is essential to delve deeper into the project’s technical documentation or any available information regarding their technology. Look for concrete use cases, real-world applications, or partnerships that demonstrate the practicality and utility of the proposed technology. Additionally, seek out independent reviews or assessments from industry experts or reputable sources. Verify if the project has conducted any pilot programs or implemented their technology in real-world scenarios. Lack of evidence or reluctance to provide concrete examples of utility should raise concerns about the legitimacy of the project.
Blockchain Explorer Analysis:
Utilize blockchain explorers to investigate the project’s token transactions and wallet addresses. By reviewing the project’s blockchain activity, you can gain insights into token distribution, large token transfers, and potentially identify suspicious wallet addresses. Analyze whether the token distribution is concentrated in a few wallets or if it is reasonably spread among a diverse group of holders. Be cautious of projects where a significant portion of tokens are held by a small number of addresses, especially if they belong to anonymous entities. Remember, a legitimate project will be able to showcase the value and practical applications of their technology, while a scam project may only offer vague promises without any substance. Prioritize projects that provide verifiable proof of utility and have a clear roadmap for integrating their technology into real-world systems or industries.
Community Feedback and Reviews:
Engage with the community surrounding the project and seek out feedback from existing participants or investors. Join relevant forums, social media groups, and chat platforms to gather insights and opinions. Pay attention to any negative experiences, complaints, or warnings shared by community members. However, be cautious of anonymous or newly created accounts, as scammers may create false personas to promote their projects or tarnish the reputation of legitimate ones. Influencers on YouTube and other platforms are often paid for reviews or endorsements of projects (sometimes not fully disclosing this fact). Even those who act ethically are not infallible and can also be tricked into thinking a project is legitimate, just like anyone else.
Here are some additional measures you can take to safeguard your interests:
Paying with Credit Cards:
I realize it is the antithesis of crypto, to not pay with crypto. However, if you are not fully trusting a project opt to use a credit card as your payment method if it’s available. Credit cards often provide more robust consumer protection measures compared to other payment methods. In the event of fraudulent activity or a dispute, credit card companies can offer chargeback options, allowing you to request a refund and investigate unauthorized transactions. If it’s a scam and you paid in crypto, you can kiss your tokens goodbye.
Be Skeptical and Trust Your Instincts:
Maintain a healthy skepticism when dealing with offers that seem too good to be true. Trust your instincts and be cautious when making financial decisions and don’t spend more than you can afford to lose.
Research and Verify:
Before engaging in any financial transactions, research the company, product, or service involved. Look for customer reviews, check the company’s reputation through reliable sources, and verify their credentials or licenses, if applicable. Be wary of companies that have a limited online presence or lack transparent information.
Protect Personal Information:
Guard your personal and financial information carefully. Avoid sharing sensitive data such as social security numbers, bank account details, or credit card information unless you are certain of the legitimacy of the recipient and the transaction. As always, be cautious of unsolicited requests for personal information, especially through emails or phone calls.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, it is important to remember that the research methods discussed in this guide are valuable tools to aid your investigation, but they do not guarantee foolproof evidence. It is crucial to consider a combination of factors and exercise critical judgment when evaluating the legitimacy of a project. By employing these research methods alongside the red flags mentioned earlier, you can enhance your ability to identify scam projects and make informed investment decisions.
While being early on a project can potentially lead to higher earnings, it also comes with increased risk. Spotting scam projects requires a skeptical mindset, and thorough research. By analyzing key indicators such as transparency, integrity, and genuine innovation, you can protect yourself from falling victim to fraudulent schemes. Always remember that due diligence and critical thinking are your best allies when navigating the cryptocurrency landscape. By following these principles, you can safeguard your investments and contribute to the growth of legitimate projects in the DePIN space.
